The anatomy of facial nerve has already been discussed in detail earlier. It is essential to have proper knowledge of anatomy to understand this section of clinical examination of facial nerve.

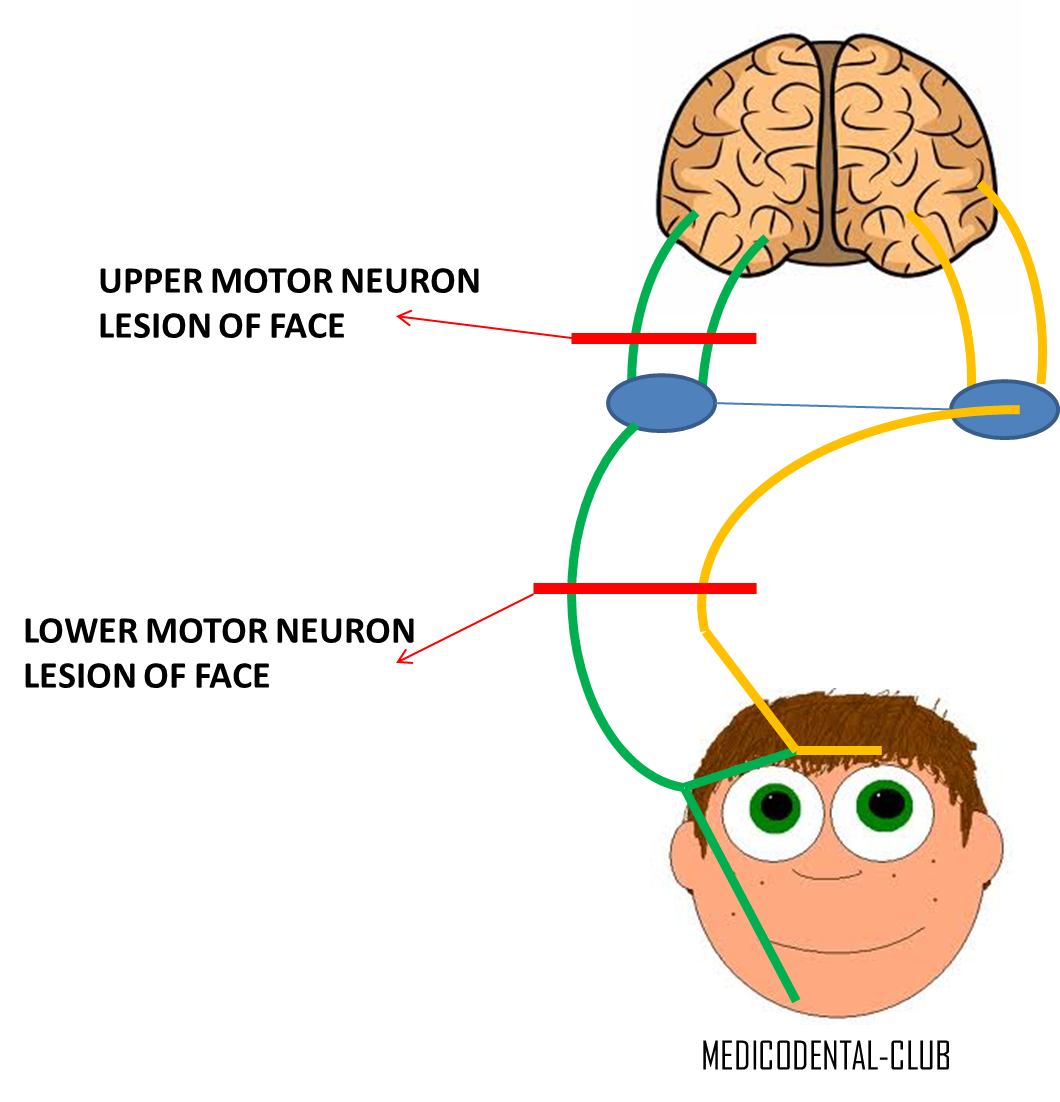
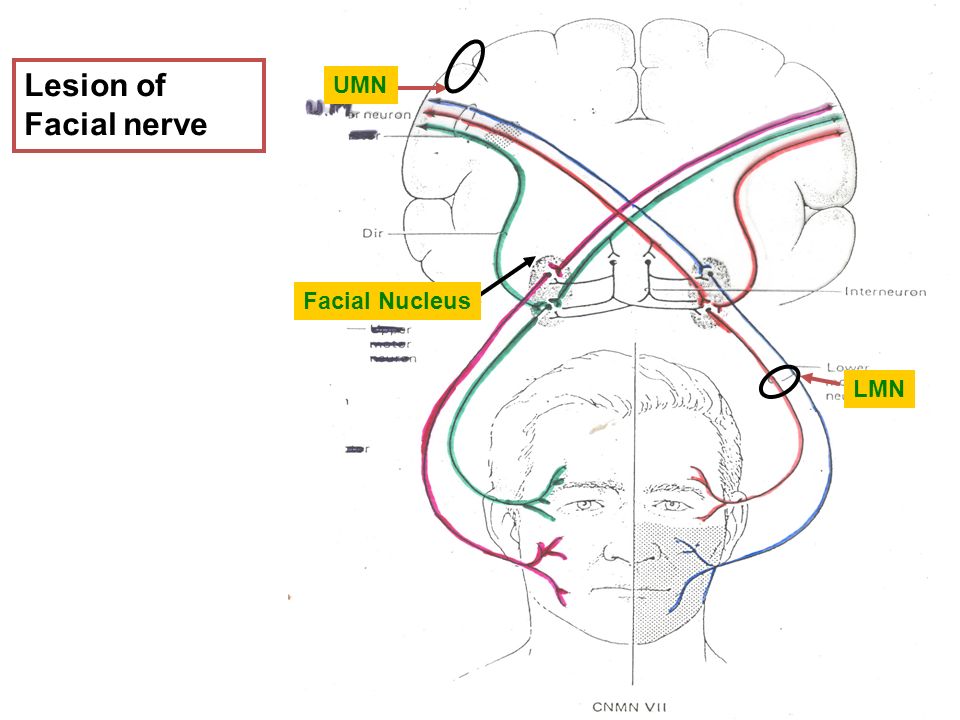
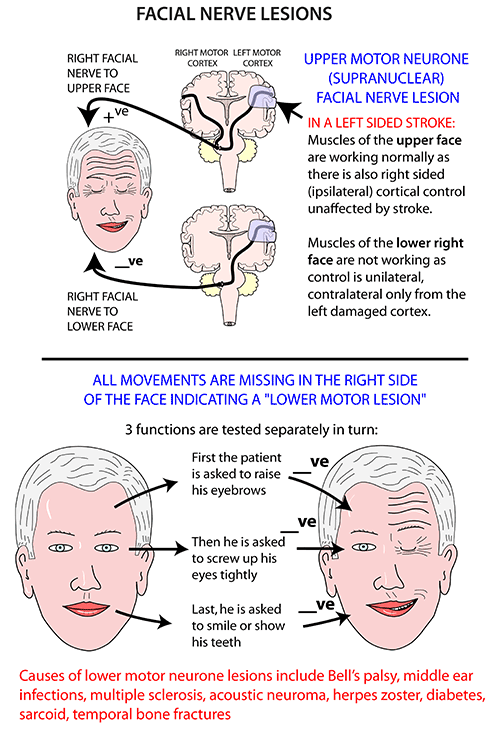
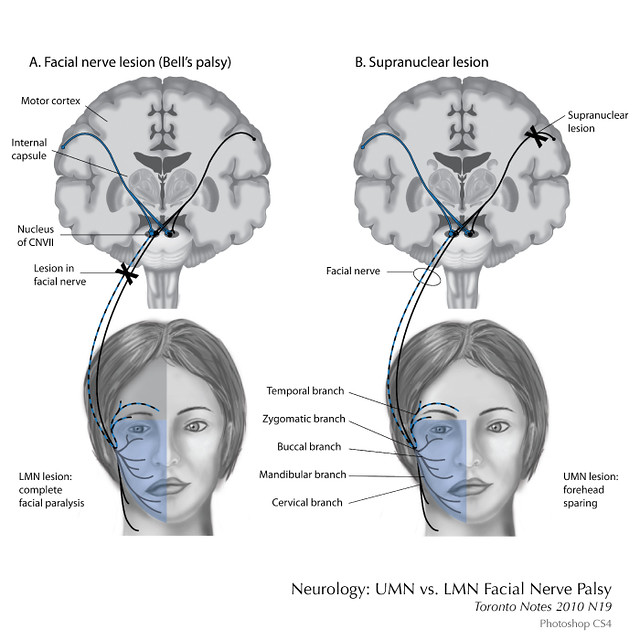
Clinical signs of facial paralysis vary with the location, severity, and chronicity of the lesion. If a unilateral lesion is located in the facial nucleus or proximal portion of the facial nerve, paresis or paralysis of the eyelids, …

by Paulette Marie Gillig, MD, PhD, and Richard D. Sanders, MD Dr. Gillig is Professor of Psychiatry and Faculty of the Graduate college, Department of Psychiatry, Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio; Dr. Sanders is Associate Professor, Departments of Psychiatry and Neurology, Boonshoft college of Medicine, Wright State University, and Ohio VA


Facial Nerve Palsy – Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the Merck Manuals – Medical Professional Version.
Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves. (“Nucleus of Facial N.” labeled at upper left.)
Facial nerve paralysis is a common problem that involves the paralysis of any structures innervated by the facial nerve.The pathway of the facial nerve is long and relatively convoluted, and so there are a number of causes that may result in facial nerve paralysis.
The facial nerve, CN VII, is the seventh paired cranial nerve. In this article, we shall look at the anatomical course of the nerve, and the motor, sensory and parasympathetic functions of its terminal branches.
Learn about the veterinary topic of Physical and Neurologic Examinations. Find specific details on this topic and related topics from the Merck Vet Manual.
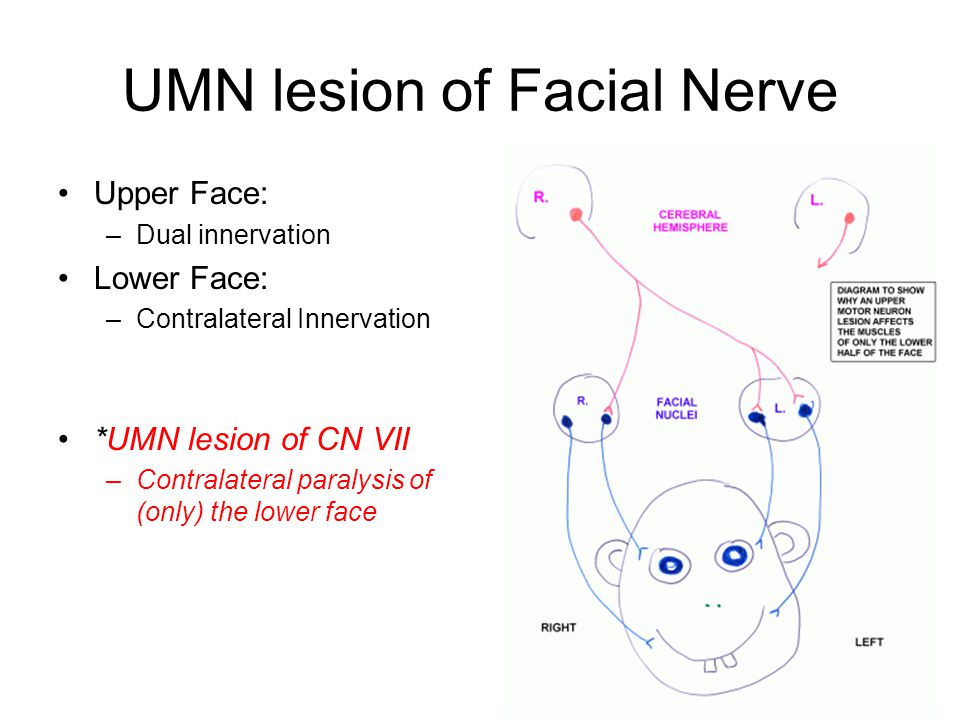
Mar 07, 2016 · Because speech, mastication, and expression of moods and emotions are based on the ability to move facial musculature—be it voluntary or involuntary—successful treatment of facial nerve paralysis is a vital concern.
Surgical, medicinal, and alternative methods for facial pain afflictions like trigeminal neuralgia, courtesy of experts from the Facial Pain Association